Singapore’s MOH and GovTech have jointly developed TraceTogether to bolster nationwide efforts against COVID-19 by enabling community-driven contact tracing. The initiative emphasizes broad smartphone participation to strengthen the tracing network, with the aim of identifying potential exposures more efficiently and quickly. The approach centers on devices exchanging proximity data when both users have the TraceTogether app installed, creating a technology-assisted layer to complement traditional public health measures. The overarching goal is to empower individuals with a practical tool that supports rapid notification and containment while preserving user privacy.
Overview of TraceTogether
Background and purpose
TraceTogether represents a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Health and GovTech to augment the country’s public health response to the COVID-19 outbreak. The system is designed as a community-driven mechanism where participating devices contribute to a shared tracing capability. By leveraging the widespread use of smartphones, the program seeks to extend reach beyond conventional manually recorded contact tracing, enabling a proactive approach to identify and interrupt transmission chains.
Core objective and user promise
At its core, TraceTogether is intended to simplify the process of tracing contacts who may have been exposed to an infected person. The concept rests on the premise that timely knowledge of close encounters can significantly shorten the window between exposure and notification, allowing for earlier testing or self-isolation. The emphasis on community participation reflects a public health strategy that relies on the collective action of residents to strengthen the overall effectiveness of the tracing system.
Ethical and privacy considerations (contextual emphasis)
A central argument for TraceTogether is that proximity data is collected in a way that supports health authorities without compromising individual privacy. By focusing on device-to-device exchanges and proximity indicators, the framework aims to minimize the need for personally identifiable information. The design underscores a balance between public health benefits and the protection of user privacy, a consideration that has been central to public communications about the app.
How TraceTogether Works
Proximity data exchange model
TraceTogether adopts a community-driven approach in which devices that have the app installed exchange proximity information with other participating devices. This exchange occurs whenever two TraceTogether-enabled devices come within detectable range of each other. The process operates continuously in the background, providing a stream of encounter data that can later be used to identify potential exposures, should a user test positive for COVID-19.
Bluetooth RSSI as a proximity proxy
The system uses Bluetooth Relative Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) readings to estimate how close two users were and how long their devices were near one another. By tracking RSSI values over time, TraceTogether attempts to approximate both the distance of a contact and the duration of the encounter. This method provides a practical proxy for proximity without requiring exact location data, aligning with privacy-preserving design goals while delivering actionable information for public health actions.
Temporal accumulation for exposure assessment
Encounters are analyzed across time to form a pattern of contact events between users. The accumulated proximity data helps determine whether an exposure threshold has been met and whether a notification should be issued to a potentially affected individual. The time dimension is essential, as it differentiates brief, incidental proximity from meaningful exposures that warrant further attention.
Data handling and privacy posture
The data ecosystem for TraceTogether emphasizes minimizing sensitive data collection and maximizing user control. Proximity information is exchanged only between devices with the app installed, and the framework is designed to avoid storing precise location data. The emphasis on privacy-sensitive design is a defining feature, aiming to reassure users that participation does not entail pervasive tracking or the disclosure of personal identifiers beyond what is essential for tracing exposure risk.
Availability and Downloads
Availability for iOS devices
TraceTogether is available for users with iOS devices, enabling installation from the official app distribution channels. The app is designed to work with iOS devices to maintain consistent performance in proximity detection and data exchanges, while respecting the privacy-oriented design principles of the system. Users with compatible iPhones and iPads can activate Bluetooth-based contact tracing through the TraceTogether app.
Availability for Android devices
For Android users, TraceTogether is also offered through official channels, ensuring broad accessibility across the Android ecosystem. The Android version adheres to the same proximity-exchange mechanism and privacy framework, providing a unified experience across major mobile platforms. The goal remains to maximize participation and coverage by accommodating the most common smartphone configurations.
General download and installation considerations
The app is positioned as a practical tool to support public health efforts, with emphasis on ease of installation and minimal friction for users. Enabling Bluetooth and granting necessary permissions are typically required steps for proper functionality. While the download process is straightforward, the broader objective is to encourage widespread adoption to strengthen the collective capability to trace contacts effectively.
Adoption, Outreach, and Public Engagement
Broad participation as a public health priority
A key message surrounding TraceTogether is the importance of broad adoption across the population. The effectiveness of a community-driven contact tracing system depends on a critical mass of users who participate and keep their devices operating with the app in the background. Public health authorities highlight the value of a widespread network in accelerating the identification of potential exposures and expediting response actions.
Encouraging widespread usage
Efforts to promote uptake focus on informing residents about the app’s role in complementing traditional tracing methods. By communicating how proximity data can help identify at-risk individuals sooner, authorities aim to foster trust and motivate users to install and maintain the app on their smartphones. Clear messaging about privacy safeguards and the public health benefits is often part of outreach campaigns.
Practical considerations for diverse communities
Recognizing varying levels of smartphone ownership and digital literacy, the program has explored complementary strategies to extend reach. For populations with limited access to smartphones, authorities have discussed alternative forms of support to ensure that vulnerable groups still benefit from exposure notification efforts, reflecting an inclusive public health approach.
Updates and Enhancements
TraceTogether 2.0: new features and insights
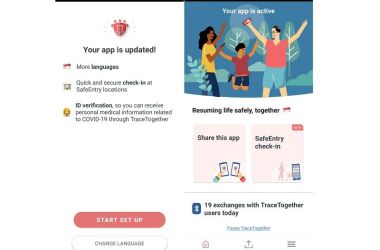
The TraceTogether platform has seen enhancements beyond its initial rollout, including the introduction of a Barcode feature and the ability to display the number of exchanges with other users. These improvements aim to provide users with tangible indicators of app activity and engagement while offering health authorities more granular insights into tracing performance. The Barcode feature introduces a new modality for representing encounter data in a scannable format, broadening how proximity information can be interpreted within a privacy-conscious framework.
TraceTogether 2.0: security and usability improvements
Alongside feature additions, the updates emphasize usability and robustness. Enhancements are designed to streamline the user experience, improve reliability of proximity detection, and reinforce trust in the system. The evolution of TraceTogether reflects an ongoing commitment to adapting the platform to real-world usage patterns and feedback from the community.
TraceTogether 2.1: background operation and QR scanning
A subsequent iteration, TraceTogether 2.1, introduces the ability for the app to operate in the background for iOS users and adds a QR scanning capability. The background operation ensures continued proximity detection even when the app is not in the foreground, improving coverage for everyday smartphone usage. The QR scanning feature provides an additional mechanism to interact with health processes, potentially facilitating quicker exposure checks and streamlined workflows for users.
Implications of updates for users and public health
These updates collectively aim to strengthen the system’s effectiveness without compromising user privacy. By expanding how data can be accessed and interpreted while maintaining a privacy-centric design, the app intends to offer more transparency and practical value to users and health authorities alike. The emphasis remains on enabling timely actions in response to exposure scenarios while preserving user trust through careful data handling.
Privacy, Security, and Trust
Data minimization and consent
TraceTogether is framed around minimal data collection with explicit consent-driven participation. The system prioritizes proximity-based data exchange rather than continuous location tracking, reducing the exposure of personally identifiable information. The privacy design seeks to reassure users that participation supports public health without unnecessary invasion of privacy.
Control and transparency
Users can expect to have visibility into how the app functions and the types of data it handles. The emphasis on transparency is intended to help users make informed decisions about their participation and to foster trust in the technology. Clear explanations about data usage, retention, and potential sharing with public health authorities are integral to the system’s governance.
Security considerations
The architecture is designed to resist unauthorized access to proximity data and to ensure that data exchanges occur securely between participating devices. Security practices aim to preserve the integrity of contact tracing information while minimizing the risk of misuse or exposure.
Challenges, Limitations, and Future Directions
Practical limitations of Bluetooth-based tracing
While Bluetooth RSSI offers a practical approach to estimating proximity, it is not a perfect measure of distance. Variability in device hardware, environments, and interference can affect accuracy. These factors are acknowledged in ongoing assessments and updates to improve reliability and user experience.
Smartphone penetration and accessibility gap
A persistent challenge is achieving comprehensive coverage across all segments of the population. While smartphone ownership is widespread, some individuals may rely on basic devices or lack consistent access to compatible hardware. Public health strategies consider these gaps by exploring supplementary measures to ensure inclusive protection and participation.
Token-based support for non-smartphone users
In recognition of accessibility challenges for certain groups, the program has explored token-based options to extend exposure notification benefits to seniors and others who may not have smartphones capable of activating the TraceTogether app. Tokens represent a complementary solution intended to protect vulnerable populations and maintain broad community engagement in tracing efforts.
Future directions and continuous improvement
The evolution of TraceTogether reflects a broader commitment to refining digital tools that support public health without compromising trust. Ongoing development focuses on expanding features, enhancing interoperability with other health systems, and ensuring that privacy protections keep pace with technical advances. The overarching aim is to sustain a resilient tracing framework that can adapt to changing circumstances while delivering tangible benefits to the population.
Conclusion
TraceTogether, a collaborative endeavor between Singapore’s MOH and GovTech, represents a strategic effort to augment nationwide contact tracing through community participation. The system relies on devices exchanging proximity information via Bluetooth RSSI to approximate the likelihood and duration of encounters, supporting more timely exposure notifications. The app is available for both iOS and Android devices, with continued updates that introduce new features such as barcode representation, exchange counts, QR scanning, and background operation on compatible platforms. Public health messaging emphasizes broad adoption, privacy-conscious design, and practical considerations to ensure accessibility and trust. As the program evolves, it remains focused on strengthening the country’s ability to respond swiftly to COVID-19 while safeguarding user privacy and promoting transparent, responsible use of the technology.